Laser Welding Cost: Breaking Down the Economics
Laser welding cost is a critical consideration for businesses looking to adopt advanced welding technologies. This article delves into the factors that influence the cost of laser welding, offering insights into its value for various industries and how to make informed decisions.
What Impacts Laser Welding Cost?
The cost of laser welding is determined by a combination of fixed, variable, and operational factors. These include equipment expenses, material type, labor, energy consumption, and maintenance.
1. Equipment Cost
The initial investment for a laser welding machine is substantial. Advanced features, automation capabilities, and power output significantly influence the price.
2. Material Compatibility
Different materials, such as stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium, require varying laser settings and parameters. This affects operational costs, as some materials demand more energy or specialized handling.
3. Labor Expenses
While laser welding often reduces the need for manual labor, skilled operators or engineers are required for setup and oversight, contributing to the overall cost.
4. Energy Consumption
The energy required to operate a laser welding system depends on the power of the machine and the duration of its use. Efficient machines may have higher upfront costs but lower long-term energy expenses.
5. Maintenance and Repairs
Regular maintenance is crucial for optimal performance. Over time, components like lenses and mirrors may need replacement, adding to operational costs.
Comparing Laser Welding Costs with Other Welding Methods
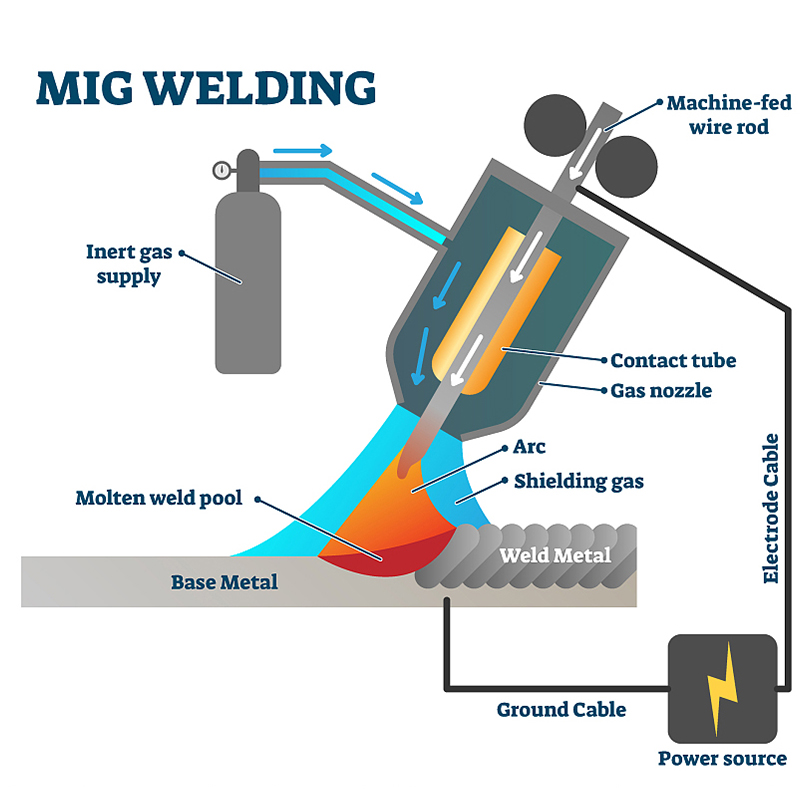
1. Laser Welding vs. MIG Welding
Laser welding offers higher precision and minimal post-processing but comes with a higher initial investment compared to MIG welding.
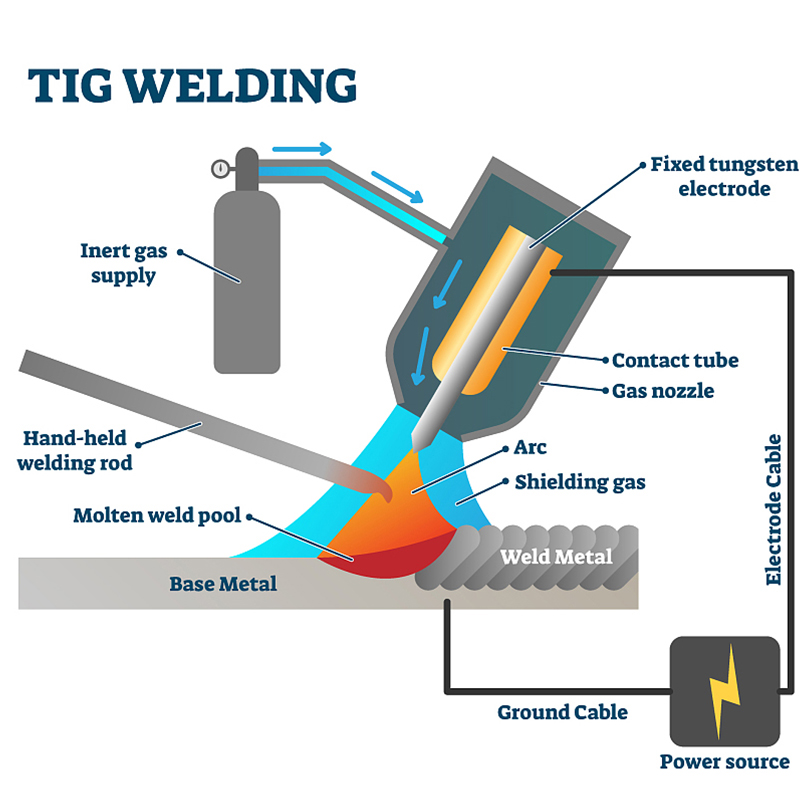
2. Laser Welding vs. TIG Welding
TIG welding is cost-effective for small-scale projects, but laser welding provides unmatched speed and consistency for large-scale manufacturing.
3. Laser Welding vs. Spot Welding
For applications requiring minimal heat-affected zones, laser welding is superior but often more expensive than traditional spot welding.
Benefits That Justify Laser Welding Costs
1. Precision and Accuracy
Laser welding delivers consistent results with minimal error, reducing material wastage and rework costs.
2. Speed and Efficiency
Automation and faster processing times result in higher throughput, offsetting the initial investment.
3. Versatility
From automotive to medical industries, laser welding is adaptable to various applications, enhancing its value.
4. Sustainability
The process produces minimal emissions and waste, aligning with green manufacturing goals.

Strategies to Optimize Laser Welding Costs
1. Invest in Energy-Efficient Equipment
Choosing energy-efficient machines reduces long-term operating expenses.
2. Utilize Automation
Automated systems decrease labor costs and improve production consistency.
3. Material Selection
Opt for materials that are easier to weld and compatible with laser technology.
4. Regular Maintenance
Preventative maintenance ensures smooth operation and avoids costly downtime.
5. Volume Production
Laser welding becomes more cost-effective as production volume increases, spreading the fixed costs over a larger output.
Applications That Maximize the Value of Laser Welding
1. Automotive Industry
Laser welding is ideal for producing lightweight, durable components, reducing overall vehicle weight.
2. Aerospace Engineering
The precision of laser welding supports the creation of high-performance, lightweight parts for aircraft and spacecraft.
3. Medical Devices
From surgical tools to implants, laser welding ensures precision and biocompatibility.
4. Electronics Manufacturing
Micro-welding for circuit boards and sensors benefits from the high accuracy of laser welding.
5. Jewelry Design
Laser welding enables intricate designs and seamless repairs in high-value jewelry.

Emerging Trends in Laser Welding
1. Hybrid Welding Systems
Combining laser welding with traditional methods enhances versatility and cost efficiency.
2. AI-Powered Optimization
Artificial intelligence is being integrated into laser systems for real-time monitoring and parameter adjustments, reducing material waste and energy usage.
3. Portable Laser Welding Machines
Compact designs are making laser welding accessible to smaller businesses and on-site applications.
4. Enhanced Cooling Systems
Advanced cooling technologies prolong machine life and improve energy efficiency.

Balancing Cost with Performance
While the upfront cost of laser welding is significant, its long-term benefits, including reduced material wastage, improved production efficiency, and higher-quality results, make it a valuable investment. By understanding the factors that influence laser welding cost and adopting strategies to optimize expenses, businesses can harness the full potential of this technology.
Laser welding is more than just an expense—it’s an investment in precision, sustainability, and innovation.


