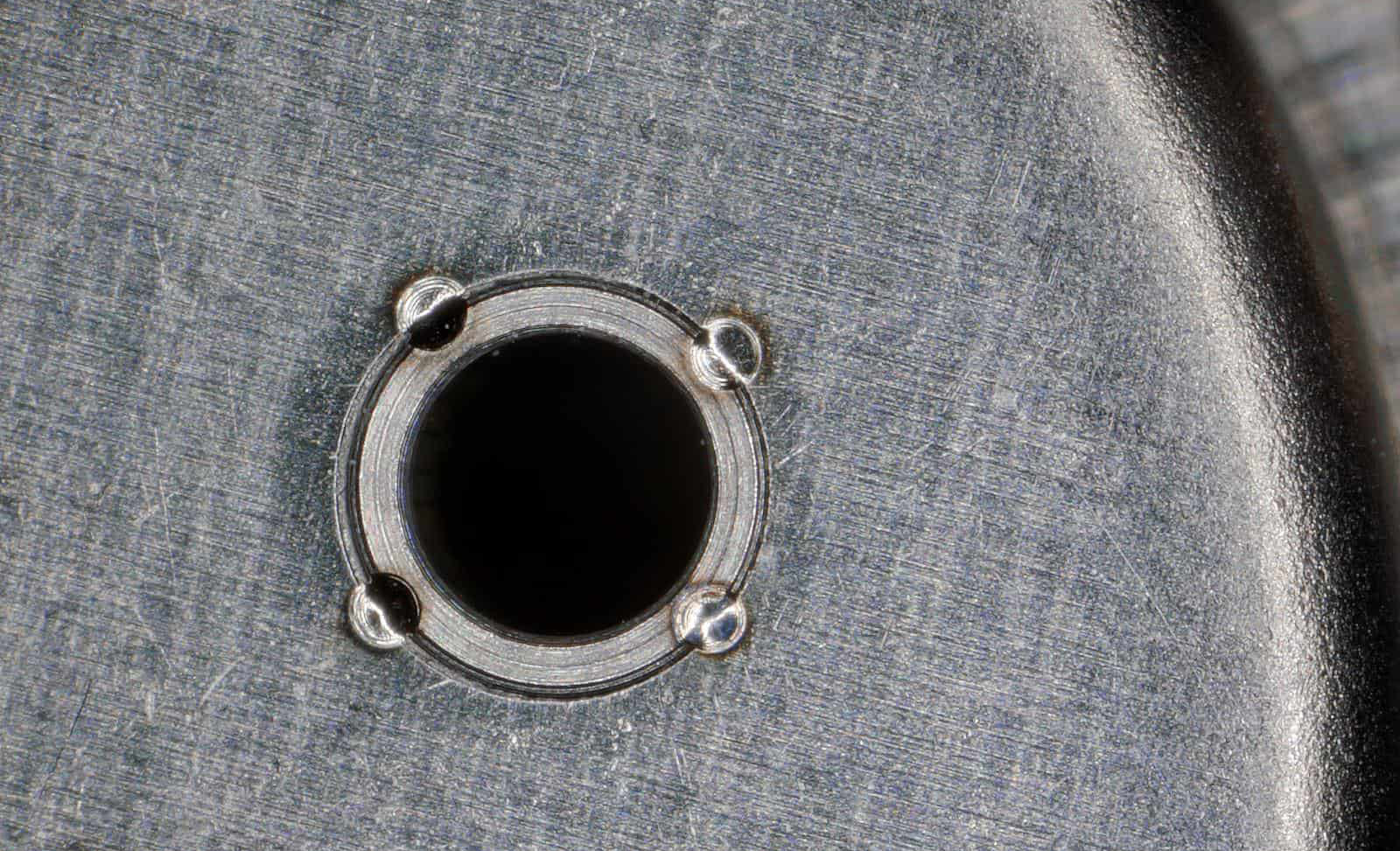

The Art and Science of Laser Micro Welding
Laser micro welding stands at the forefront of precision engineering, bridging gaps and fusing materials with microscopic accuracy. It is a transformative technology that has found its way into industries demanding unparalleled precision, such as electronics, medical devices, and aerospace.
What is Laser Micro Welding?
Laser micro welding is a technique that utilizes highly focused laser beams to join materials at a microscopic scale. This process enables the creation of strong, precise welds, often invisible to the naked eye, making it ideal for intricate components and assemblies.
How Does Laser Micro Welding Work?
1. Laser Source Generation
The process begins with a laser source, typically a fiber or pulsed laser, which emits a highly focused beam of light.
2. Beam Focus
The laser beam is directed through optical lenses to concentrate its energy onto a specific point.
3. Heat Application
The intense heat generated by the laser melts the material surfaces at the joint, creating a molten pool.
4. Material Fusion
As the molten material cools and solidifies, a strong and seamless weld is formed.
5. Monitoring and Control
Advanced systems monitor parameters such as beam intensity, duration, and focus to ensure consistency.
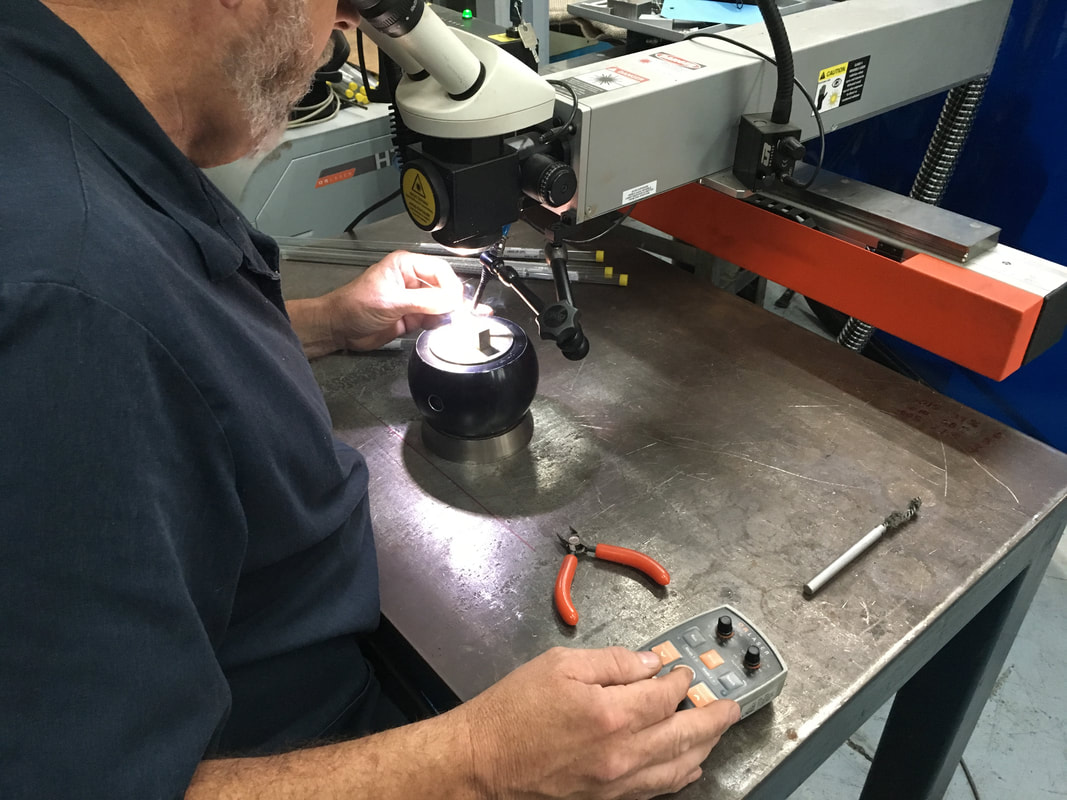

Key Features of Laser Micro Welding
1. Precision
Laser micro welding achieves sub-micron accuracy, allowing for the creation of delicate and intricate welds.
2. Minimal Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ)
The focused heat minimizes thermal damage to surrounding areas, preserving the integrity of the material.
3. Non-Contact Process
The laser never touches the material, reducing wear and the need for physical tools.
4. Versatility
It works effectively with a wide range of materials, including metals, alloys, and even dissimilar materials.
Applications of Laser Micro Welding
1. Electronics Industry
Used for assembling miniature components like microchips, sensors, and circuit boards.
2. Medical Devices
Enables the production of surgical tools, implants, and other critical devices.
3. Aerospace Engineering
Ideal for creating lightweight, durable components for spacecraft and aircraft.
4. Jewelry and Luxury Goods
Allows for precision repairs and custom designs without visible seams.
5. Automotive Industry
Essential for micro-welding sensors and small parts in modern vehicles.
Benefits of Laser Micro Welding
1. High Strength Welds
Produces welds with superior mechanical properties, ensuring long-lasting performance.
2. Reduced Material Waste
The precision of the process minimizes excess material usage.
3. Increased Productivity
Automated systems allow for faster production cycles without compromising quality.
4. Environmental Friendliness
The process is energy-efficient and produces minimal waste, aligning with sustainable practices.
Challenges in Laser Micro Welding
1. High Initial Costs
The equipment required for laser micro welding can be expensive, though long-term benefits often justify the investment.
2. Operator Training
Specialized skills are needed to operate and maintain the equipment effectively.
3. Material Compatibility
Some materials may require additional preparation or surface treatments to ensure successful welding.
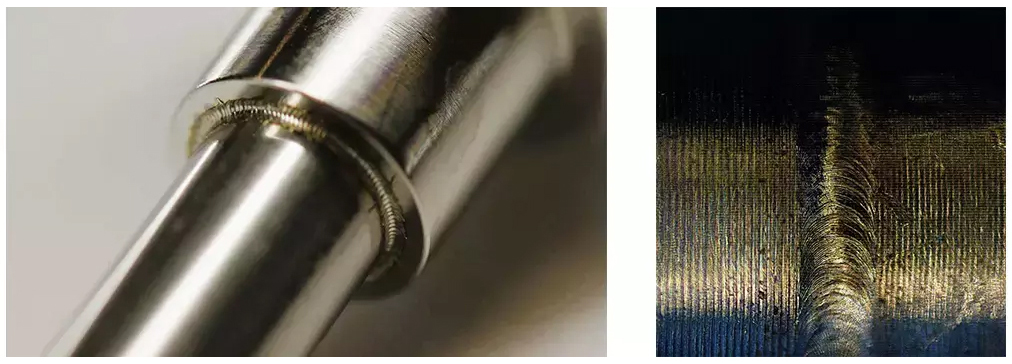
Innovations in Laser Micro Welding
1. AI-Driven Systems
Artificial intelligence is being integrated to optimize weld quality and adjust parameters in real-time.
2. Hybrid Welding Techniques
Combining laser micro welding with other welding methods enhances flexibility and capabilities.
3. Compact and Portable Designs
Newer machines are designed to be smaller and more mobile, increasing accessibility.
4. Advanced Cooling Mechanisms
Improved cooling systems ensure prolonged operation without overheating.
Choosing the Right Laser Micro Welding Machine
1. Application Requirements
Understand the specific needs of your projects, such as material type and weld size.
2. Power and Precision
Select a machine with the appropriate power output and precision capabilities for your applications.
3. Scalability
Choose equipment that can grow with your business and handle increasing demands.
4. Budget Considerations
Balance initial costs with long-term benefits, including maintenance and operational efficiency.

Environmental Impact
Laser micro welding contributes to sustainable manufacturing by reducing energy usage and material waste. Its precision also supports the production of energy-efficient devices and lightweight components.
Future Trends in Laser Micro Welding
1. Advanced Materials
Research is focused on expanding the range of compatible materials, including composites and bio-compatible substances.
2. IoT Integration
The use of IoT in welding machines allows for remote monitoring and diagnostics.
3. Full Automation
Automation continues to enhance productivity and reduce human error in micro welding processes.
4. Cost Reduction
Technological advancements are expected to make laser micro welding more affordable for small and medium enterprises.
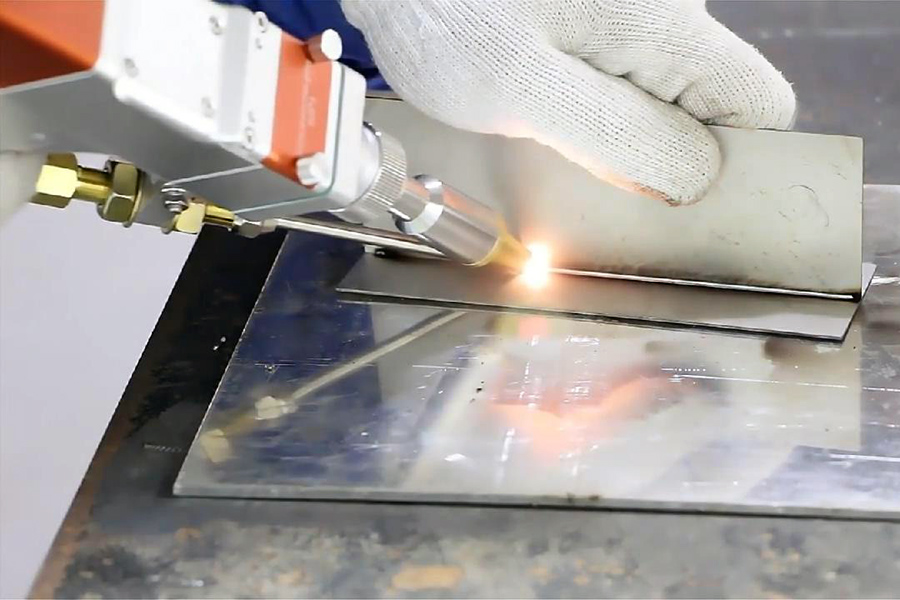

Insights for Industry Professionals
For professionals in manufacturing and precision industries, mastering laser micro welding can lead to greater efficiency and innovation. By understanding the capabilities and potential of this technology, businesses can maintain a competitive edge while meeting the growing demands for precision and sustainability.



