Laser Cutting and Welding Machines: The Technology Behind Precision
Laser cutting and welding machines combine precision, speed, and adaptability, making them indispensable in industries ranging from automotive to aerospace. Understanding how these machines operate and their wide-ranging applications offers insight into why they are redefining manufacturing processes.
What is a Laser Cutting and Welding Machine?
A laser cutting and welding machine is a high-tech device designed to cut and weld materials with unparalleled accuracy. These machines employ concentrated laser beams to melt, cut, or join materials like metals, plastics, and composites, delivering superior results compared to traditional methods.
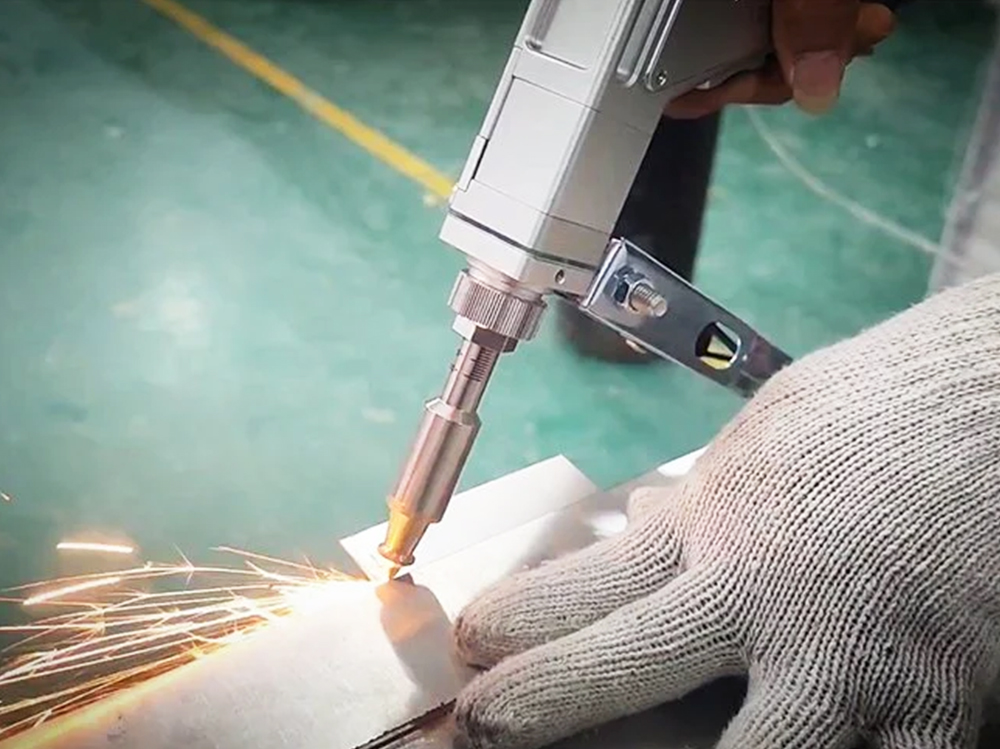
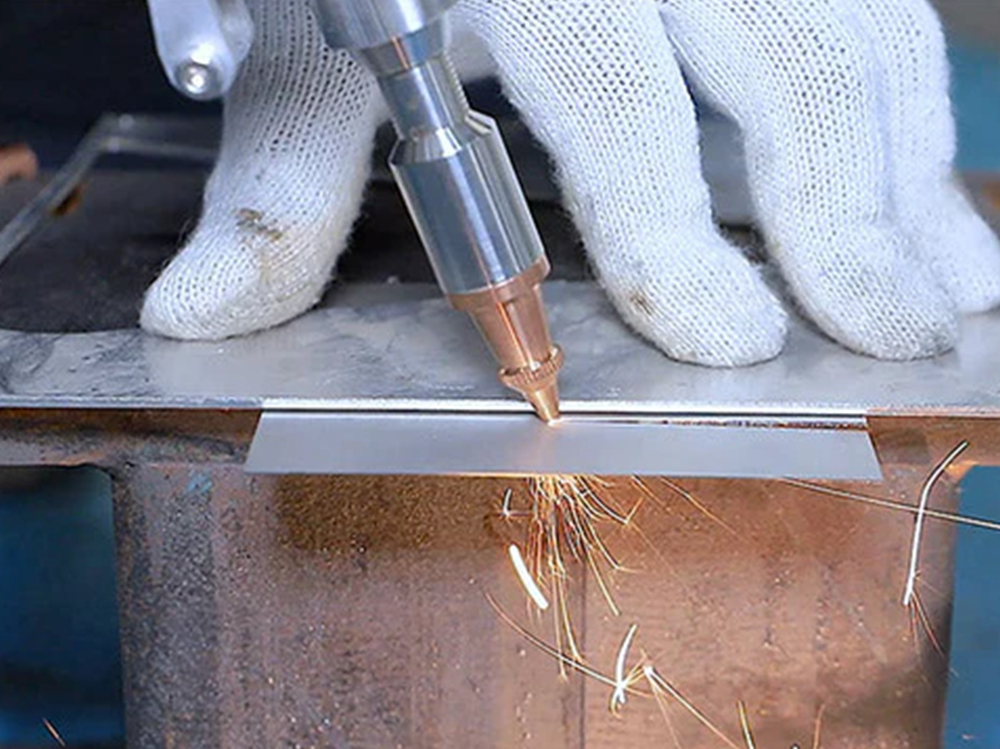


How Do Laser Cutting and Welding Machines Work?
1. Laser Generation
The process begins with a powerful laser source, such as a CO2 or fiber laser, which generates the concentrated light beam.
2. Beam Delivery System
The laser beam is directed through optical components to focus it on the material’s surface. This ensures the energy is concentrated on a precise point for cutting or welding.
3. Cutting Process
In cutting, the laser beam melts or vaporizes the material along a predefined path, producing clean and accurate cuts.
4. Welding Process
For welding, the beam heats the materials at the joint, creating a molten pool that solidifies into a seamless weld.
5. Real-Time Monitoring
Advanced systems use sensors to monitor the process and adjust parameters, ensuring consistency and quality.
Key Advantages of Laser Cutting and Welding Machines
1. Unmatched Precision
These machines achieve micron-level accuracy, making them ideal for intricate designs and small components.
2. Versatility
Capable of working with a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites, they adapt to diverse industrial needs.
3. High Efficiency
Laser machines significantly reduce production time while maintaining high-quality output.
4. Reduced Material Waste
The precision of laser processes minimizes material waste, making them environmentally and economically sustainable.
5. Non-Contact Processing
Since the laser doesn’t physically touch the material, there’s minimal wear and tear on the machine components.

Applications of Laser Cutting and Welding Machines
1. Automotive Industry
Used to cut and weld components like chassis, doors, and exhaust systems, ensuring structural integrity.
2. Aerospace Sector
Essential for creating lightweight and durable parts for aircraft and spacecraft.
3. Electronics Manufacturing
Facilitates the precise assembly of circuit boards and electronic components.
4. Medical Equipment
Enables the production of surgical instruments and implants with high precision.
5. Renewable Energy
Plays a critical role in manufacturing parts for wind turbines and solar panels.
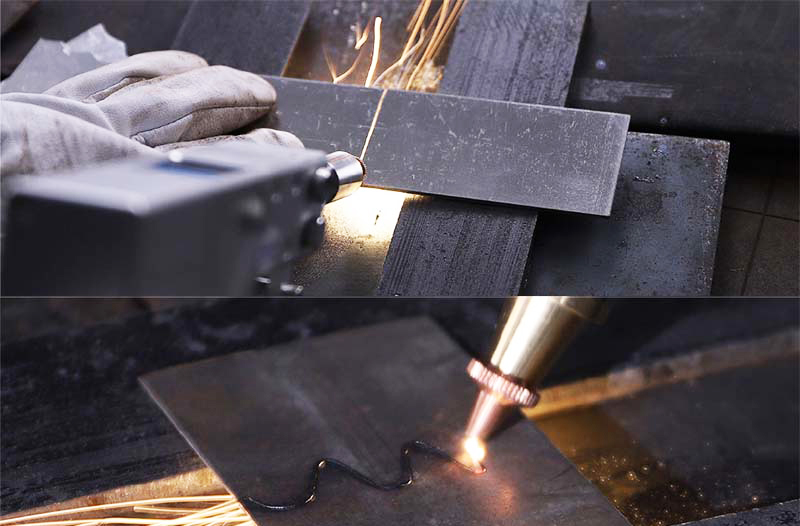

Challenges and Considerations
1. High Initial Costs
The advanced technology comes with a significant upfront investment, though the long-term benefits outweigh the cost.
2. Maintenance
Regular maintenance of optical components and laser sources is crucial to ensure consistent performance.
3. Operator Expertise
Operating these machines requires specialized training to maximize their potential and minimize errors.
4. Reflective Materials
Highly reflective materials, such as certain metals, can cause laser energy loss, necessitating advanced equipment.
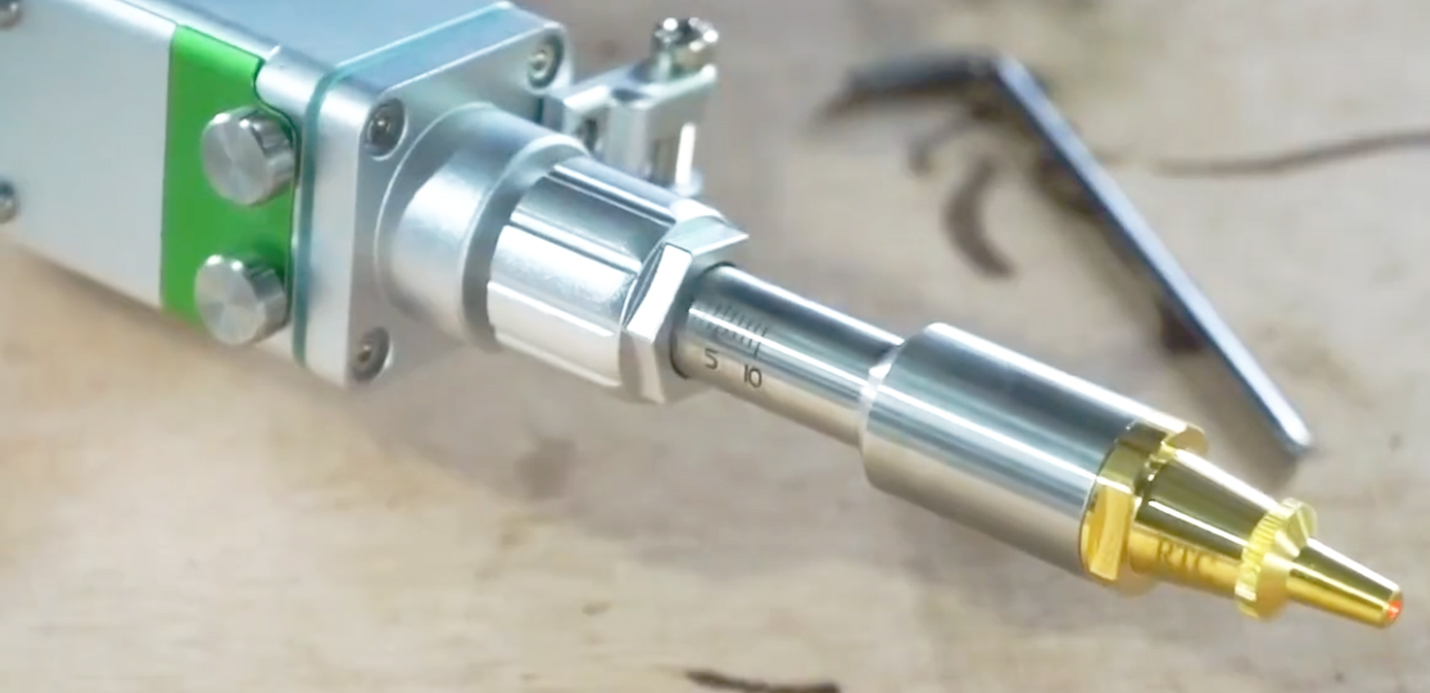

Innovations in Laser Technology
1. Hybrid Systems
Combining laser cutting and welding in a single machine enhances efficiency and reduces equipment needs.
2. AI Integration
Artificial intelligence optimizes machine settings in real-time, improving accuracy and reducing material waste.
3. Compact Designs
Newer models are smaller and more portable, making them accessible for small-scale industries.
4. Enhanced Cooling Systems
Improved cooling systems extend machine lifespan and prevent overheating during prolonged use.
How to Choose the Right Machine
1. Understand Your Needs
Define the materials you work with and the processes you require, such as cutting, welding, or both.
2. Power Requirements
Select a machine with the appropriate power rating for the thickness and type of materials you handle.
3. Budget Considerations
Factor in initial costs, maintenance, and operational expenses when making your decision.
4. Future Scalability
Choose a machine that can accommodate your growing production demands and evolving industry standards.

Environmental and Economic Benefits
Laser cutting and welding machines contribute to sustainable manufacturing by reducing energy consumption and minimizing waste. Their ability to create durable, lightweight components supports energy-efficient designs in transportation and construction.
Future Trends
1. IoT-Enabled Machines
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology allows for remote monitoring and diagnostics, improving efficiency.
2. Broader Material Compatibility
Research aims to expand the range of materials suitable for laser processes, opening new possibilities.
3. Automation and Robotics
Automation will further streamline processes, enabling 24/7 operation with minimal human intervention.
4. Accessible Pricing
As technology advances, the cost of laser machines will decrease, making them viable for smaller businesses.
Insights for Industry Professionals
For professionals in manufacturing, understanding the capabilities of laser cutting and welding machines can lead to better decision-making and operational efficiency. By investing in these technologies, businesses can achieve higher quality standards and maintain a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market.

