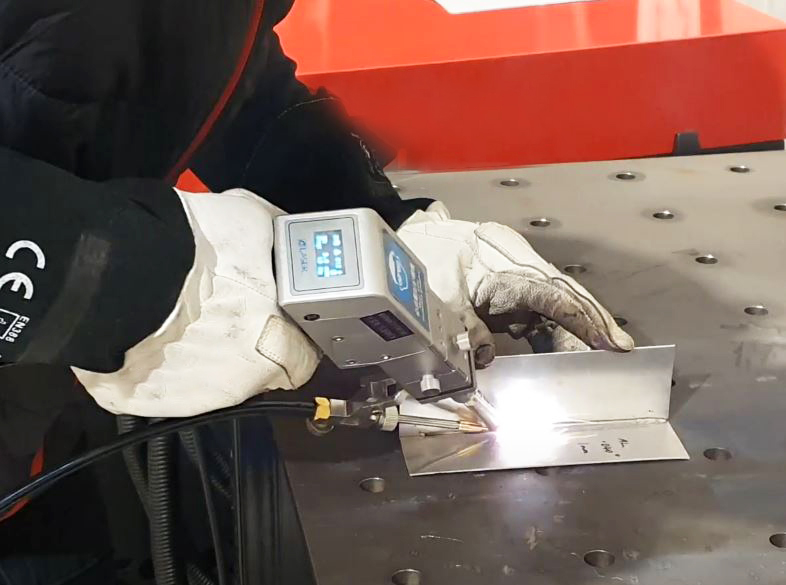

Laser Aluminum Welder: A Revolutionary Tool for Precision and Efficiency
Laser aluminum welders represent a significant leap in welding technology, providing unmatched precision and versatility for modern manufacturing needs. Whether you’re an industry professional or simply curious, understanding how these machines operate can unlock new perspectives on their capabilities and benefits.
What Is a Laser Aluminum Welder?
A laser aluminum welder uses a concentrated laser beam to join aluminum components with exceptional accuracy. The process involves focused energy, which melts and fuses the aluminum surfaces, creating a strong and seamless bond.
How Does a Laser Aluminum Welder Work?
1. Laser Generation
The process starts with a high-powered laser source, such as a fiber or diode laser. The laser generates an intense beam of light capable of melting aluminum at high temperatures.
2. Beam Delivery and Focusing
The laser beam is directed through optical systems, including lenses and mirrors, to focus it on the aluminum surface. This focused beam ensures minimal energy loss and precise targeting.
3. Material Interaction
When the laser beam strikes the aluminum, it generates localized heat that melts the material. The molten aluminum fuses, and upon cooling, forms a robust joint.
4. Cooling and Solidification
As the molten aluminum cools, it solidifies into a durable, corrosion-resistant weld, often requiring no post-processing.
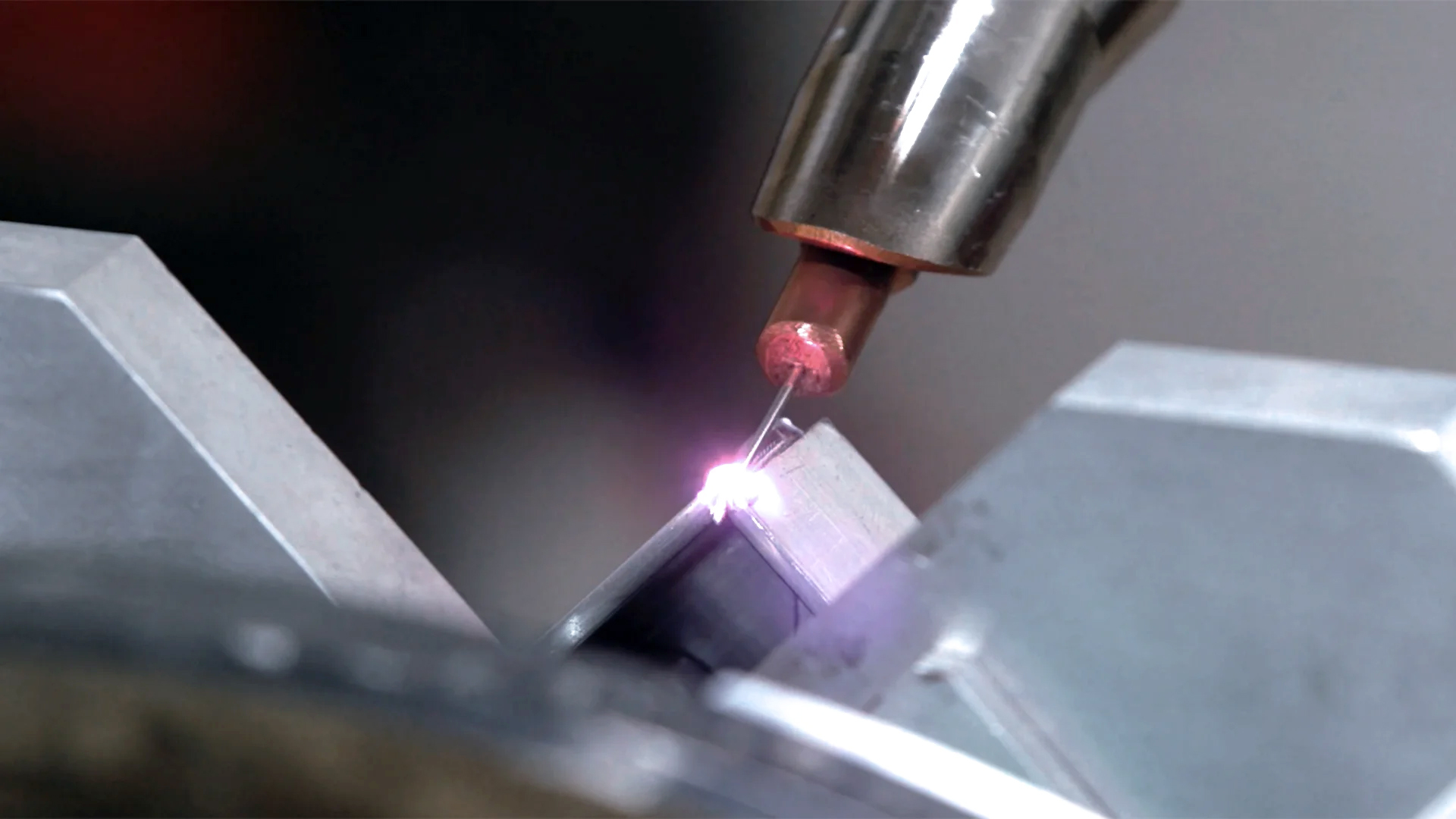
Advantages of Using Laser Aluminum Welders
1. High Precision
Laser aluminum welders deliver pinpoint accuracy, making them ideal for intricate designs and small-scale applications.
2. Speed and Efficiency
These welders complete tasks rapidly, significantly reducing production times while maintaining quality.
3. Minimal Distortion
The localized heating minimizes heat-affected zones (HAZ), preserving the structural integrity of the aluminum.
4. Versatility
They can weld a wide range of aluminum alloys, including those challenging for traditional methods.
5. Clean and Aesthetic Welds
Laser welders produce visually appealing joints that often eliminate the need for secondary finishing.

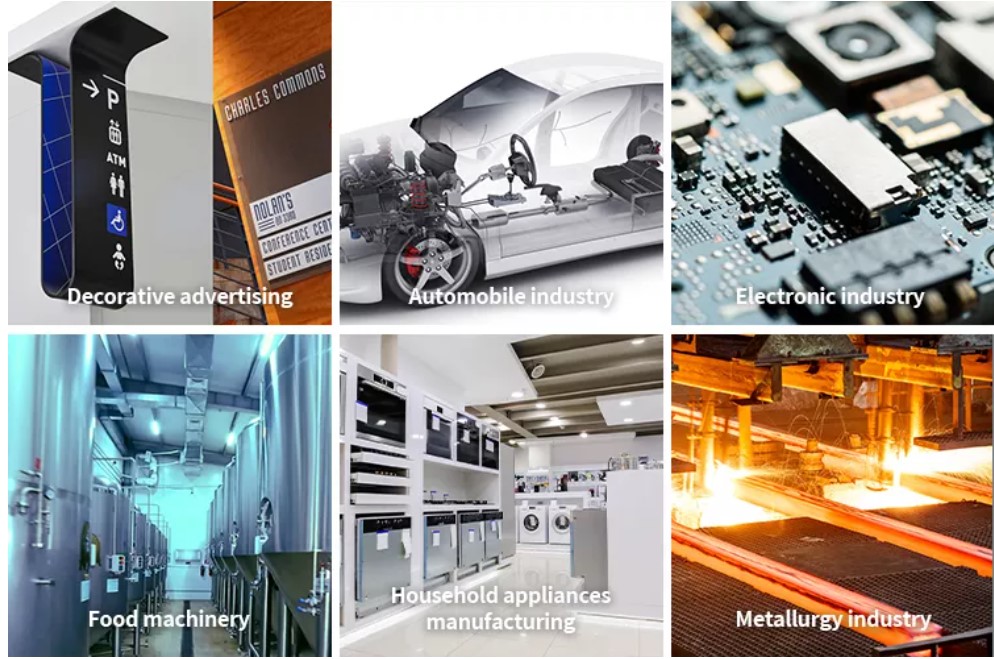
Applications of Laser Aluminum Welders
1. Automotive Industry
Used for assembling lightweight yet strong vehicle components, such as frames and panels.
2. Aerospace Engineering
Ideal for creating reliable welds in aluminum parts for aircraft and spacecraft.
3. Electronics Manufacturing
Enables the precise joining of aluminum components in compact devices.
4. Renewable Energy
Plays a vital role in welding aluminum parts for solar panels and wind turbines.
5. Consumer Goods
Used in producing high-quality aluminum goods, such as appliances and furniture.
Challenges and Limitations
1. High Initial Costs
Laser aluminum welders require a significant upfront investment, although their long-term efficiency offsets the cost.
2. Sensitivity to Reflectivity
Aluminum’s high reflectivity can cause laser energy loss, necessitating advanced equipment to ensure efficiency.
3. Maintenance Requirements
Optical components like lenses and mirrors require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
4. Operator Training
Operators must have specialized knowledge to handle the equipment and optimize settings for various aluminum alloys.
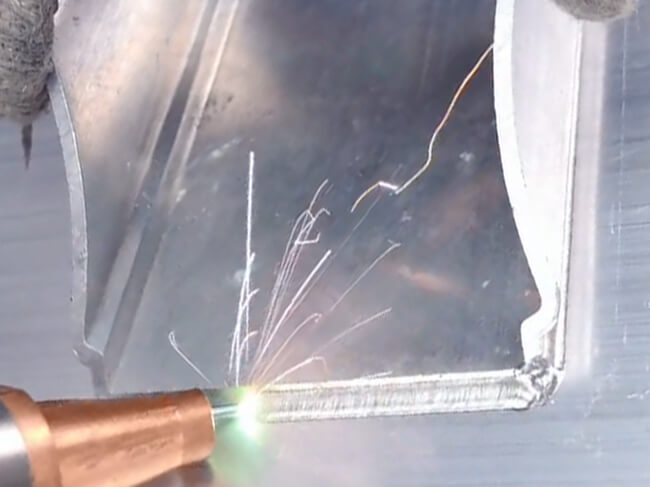
Innovations in Laser Aluminum Welding
1. Advanced Beam Shaping
Modern welders allow real-time adjustments to the beam profile, optimizing weld quality for specific aluminum types.
2. AI-Powered Control Systems
Artificial intelligence enhances precision and efficiency by adjusting parameters based on real-time feedback.
3. Compact and Portable Designs
Newer models are smaller and more portable, expanding their usability across industries.
4. Improved Cooling Systems
Efficient cooling systems prevent overheating and extend equipment lifespan.
How to Choose the Right Laser Aluminum Welder
1. Power Requirements
Consider the power level needed based on the thickness and type of aluminum you plan to weld.
2. Application Type
Select a welder with features tailored to your specific industry needs, such as portability or automation capabilities.
3. Compatibility with Alloys
Ensure the welder can handle the aluminum alloys you use in your projects.
4. Budget and Maintenance
Factor in not only the purchase cost but also ongoing maintenance expenses.

Environmental and Economic Impact
Laser aluminum welders support sustainable manufacturing by minimizing energy consumption and reducing material waste. Their ability to produce strong, lightweight components contributes to energy-efficient designs in transportation and construction.
Future Trends in Laser Aluminum Welding
1. Wider Adoption of Automation
Automation will further streamline laser aluminum welding processes, enhancing speed and consistency.
2. Improved Alloy Compatibility
Research aims to expand the range of aluminum alloys suitable for laser welding, unlocking new applications.
3. Enhanced Accessibility
As technology advances, laser aluminum welders will become more affordable and user-friendly, encouraging widespread adoption.
4. IoT-Enabled Systems
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) technology will enable remote monitoring and diagnostics, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
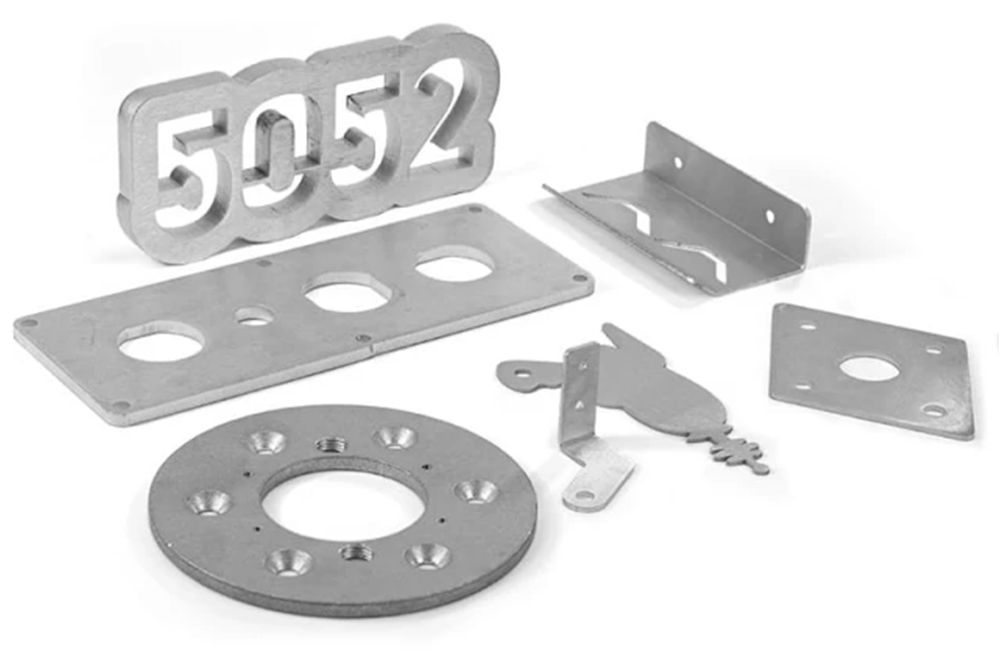

Insights for Professionals
For those considering a laser aluminum welder, understanding its capabilities and applications is key to maximizing investment. By aligning the machine’s features with your operational goals, you can achieve unparalleled efficiency, quality, and profitability.



