How Does Laser Cleaning Work? A Comprehensive Exploration
In a world where innovation drives efficiency, laser cleaning emerges as a game-changing solution. The question many ask is, how does laser cleaning work? This advanced technique is transforming industries by offering a precise, eco-friendly, and highly effective way to clean surfaces.
What is Laser Cleaning?
Laser cleaning is a cutting-edge method of removing contaminants, such as rust, paint, and grease, from surfaces using focused laser beams. Unlike traditional methods, laser cleaning is non-contact and non-abrasive, ensuring the integrity of the underlying material.
How Does Laser Cleaning Work?
1. The Principle of Laser Ablation
The primary mechanism behind laser cleaning is laser ablation. A high-energy laser beam is directed onto the contaminated surface, where it interacts with the contaminants. These materials absorb the laser energy, causing them to heat up, break apart, and vaporize or detach from the surface.
2. The Role of Material Properties
Different materials absorb laser energy differently. Metals, for example, reflect most of the laser energy, while contaminants like rust absorb it, making laser cleaning highly selective.
3. The Cleaning Process
• Emission: A laser beam is emitted and directed at the surface.
• Interaction: Contaminants absorb the laser energy, breaking down molecular bonds.
• Removal: The debris is either vaporized or gently displaced, leaving the surface clean.
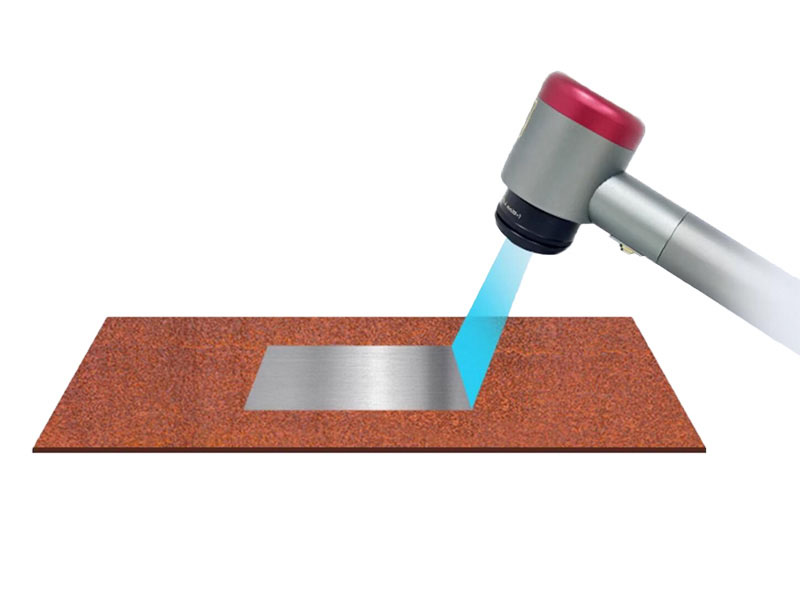
Types of Laser Cleaning
1. Pulsed Laser Cleaning
Uses short, high-energy pulses to remove contaminants. Ideal for delicate applications like restoring historical artifacts.
2. Continuous Wave Laser Cleaning
Employs a steady laser beam for cleaning larger, less sensitive surfaces, such as industrial equipment.

Advantages of Laser Cleaning
1. Eco-Friendly: Eliminates the need for chemicals, reducing environmental impact.
2. Precision: Allows for targeted cleaning without damaging the substrate.
3. Cost-Effective: Reduces labor, material, and maintenance costs over time.
4. Versatile: Applicable across industries, including automotive, aerospace, and heritage restoration.
5. Non-Abrasive: Ensures the original surface remains intact.
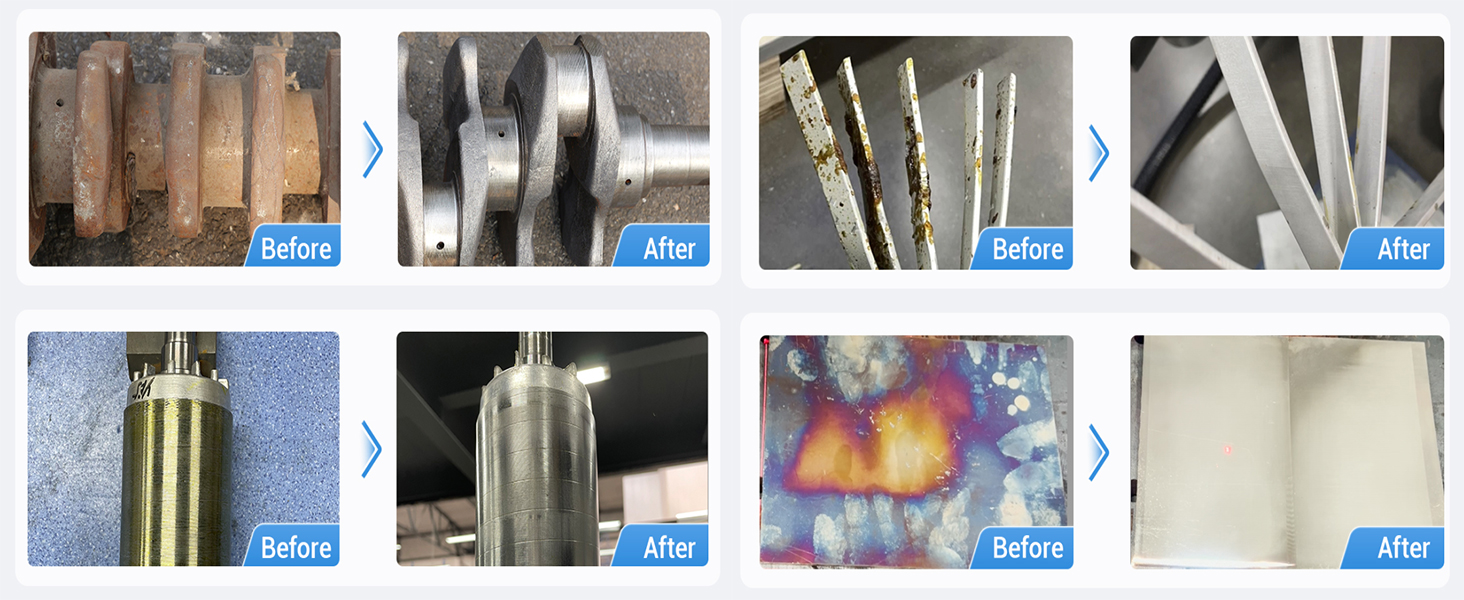
Applications of Laser Cleaning
1. Rust Removal
Efficiently removes rust from metal surfaces, restoring them to their original state.
2. Paint Stripping
Precisely removes paint layers without harming the base material.
3. Mold Cleaning
Ideal for cleaning industrial molds used in manufacturing processes.
4. Historical Restoration
Safely cleans artifacts and monuments without causing damage.
5. Surface Preparation
Prepares surfaces for welding, coating, or other treatments.

Comparison with Traditional Cleaning Methods
| Feature | Laser Cleaning | Traditional Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Minimal | High |
| Precision | High | Moderate |
| Surface Damage | None | Possible |
| Consumable Costs | Low | High |
Factors Affecting Laser Cleaning Efficiency
1. Laser Power
Higher power levels enable faster and more thorough cleaning but may not be suitable for delicate surfaces.
2. Contaminant Type
The nature and thickness of the contaminants influence the effectiveness of laser cleaning.
3. Surface Material
Reflective surfaces like polished metals may require specific laser settings for optimal cleaning.
Why Industries Choose Laser Cleaning
Industries worldwide are turning to laser cleaning for its unmatched benefits. It not only enhances operational efficiency but also aligns with sustainability goals. From reducing downtime in manufacturing to preserving cultural heritage, the applications are vast and impactful.

The Future of Laser Cleaning Technology
1. Advanced AI Integration
Future laser cleaning machines may use AI to automatically adjust settings for optimal cleaning based on material and contaminant type.
2. Increased Portability
The development of lighter, more compact machines will expand the usability of laser cleaning.
3. Enhanced Energy Efficiency
Innovations in laser technology aim to reduce energy consumption while maintaining performance.
How to Get Started with Laser Cleaning
1. Understand Your Requirements: Assess the type of surfaces and contaminants you deal with.
2. Choose the Right Machine: Select a laser cleaning machine with appropriate power and features.
3. Train Your Team: Ensure operators are trained in laser cleaning technology to maximize efficiency.
4. Maintenance and Safety: Regularly maintain your equipment and adhere to safety guidelines to ensure longevity and safe operation.
Laser cleaning represents the future of surface cleaning, combining precision, efficiency, and environmental responsibility. By understanding how it works and its potential applications, industries can harness its full potential to achieve cleaner, safer, and more sustainable operations.


